Machine Translation Tools: Comprehensive BLEU Evaluation

The language services industry offers an intimidating array of machine translation options. To help you separate the truly innovative from the middle-dwellers, your pals here at Lilt set out to provide reproducible and unbiased evaluations of these options using public data sets and a rigorous methodology.
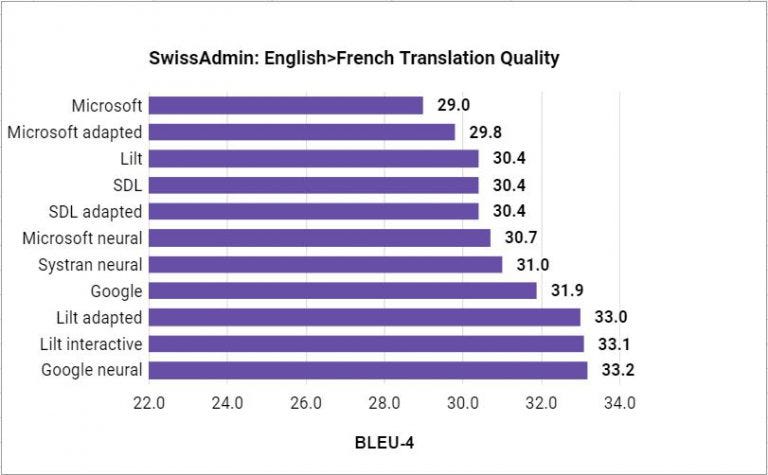
This evaluation is intended to assess machine translation not only in terms of baseline translation quality, but also regarding the quality of domain adapted systems where available. Domain adaptation and neural networks are the two most exciting recent developments in commercially available machine translation. We evaluate the relative impact of both of these technologies for the following commercial systems:
- Google's Phrase-based API
- Google Neural (GNMT)
- Microsoft Translator API/Microsoft Adapted
- Systran "Pure Neural MT "
- SDL “AdaptiveMT” system
- SDL Adapted
We also include three results from our own systems:
- Lilt — Translations from Lilt before any translation memory is uploaded or the system is used.
- Lilt Adapted — Translations from Lilt using a relevant translation memory for domain adaptation.
- Lilt Interactive — Translations from Lilt using a relevant translation memory for domain adaptation and corrected translations for each confirmed segment.
Translation quality is measured using the BLEU metric, the most common evaluation metric in machine translation research, which measures the similarity between proposed translations and reference translations. Higher numbers correspond to better translations.
Our evaluation on over 1,000 segments, chosen carefully to be representative of professional translation work, clearly shows that the new technologies of neural and adaptive translation are not just hype, but provide substantial improvements in machine translation quality.
To see the full evaluation, more details on each system in question, and more on how to interpret the results click the button below for access to the full report.