Case Study: First Large-Scale Application of Auto-Adaptive MT

Combining Machine Translation (MT) with auto-adaptive Machine Learning (ML) enables a new paradigm of machine assistance. Such systems learn from the experience, intelligence and insights of their human users, improving productivity by working in partnership, making suggestions and improving accuracy over time.
The net result is that human reviewers produce far higher volumes of content, with nearly the same level of quality, for a fraction of the time and cost. Machine assistance can save customers up to one half (or more) of the price of traditional high-quality human translation services. Or, if you’ve been used to machine translation alone and have been unhappy with the results, watch your translation quality rise dramatically with a marginal increase in price.
Case Study: Travel Portal Translation
A large travel and tour web site wanted to localize 1.77 million words of content from their catalog into 6 languages within a two week window. The hard deadline was to be ready to accommodate the summer vacation plans of millions of global users with more destinations and new activities. Successfully achieving this goal required rapid mobilization of a high-quality team of humans, fully-empowered by robust machine assistance technology.
e2f, based out of San Jose, California, with over 15 years of success in the translation and localization business, provided the “human capital” for the project. Their team was comprised of 100+ experienced translators, editors, and reviewers, plus seven project managers and a senior localization engineer.
Lilt, based out of Palo Alto, California, provided the translation engine for the project. Founded in 2015, its technology platform incorporates the latest research in Natural Language Processing (NLP), Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), and Machine Learning (ML).
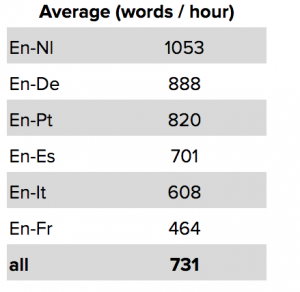
The Lilt platform proved invaluable in augmenting e2f’s human staff, increasingly translation speeds far beyond the industry average of 335 words per hour. The automation process required transformation of source Excel documents into a format suitable for automated processing, which were then uploaded into the correct accounts in Lilt via scripts calling Lilt’s APIs. Once translations were made within the Lilt system, output was generated and transformed back into Excel documents in the target languages.
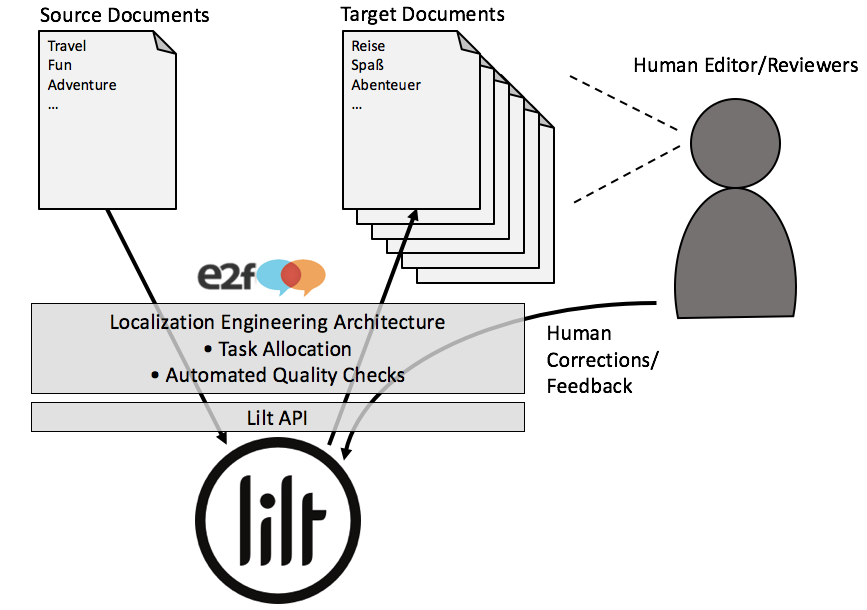
Human translators could then accept or revise these segments. If Lilt’s suggestions were rejected, the approved human translations were fed back into the system, which learned from the human’s perspective and expertise. This positive feedback loop enabled faster and more accurate translation over time as the human translators contextually taught the system preferred translations of terms and phrases.
The client’s reaction was overwhelmingly positive. The number of errors was low compared to traditional machine translation solutions and the quality in line with standard human translations. Given a two-week window, the project was actually completed within 10 days.
Lilt’s productivity gains helped us submit the winning bid on the largest translation project in our company’s history, and deliver both ahead of schedule and within budget.
— Michel Lopez, CEO, e2f
This was the first time ever that teams of translators were training an MT system collectively, interactively and in real-time. The project proved that auto-adaptive machine translation technology is ready for large-scale production use.
— Spence Green, CEO, Lilt


